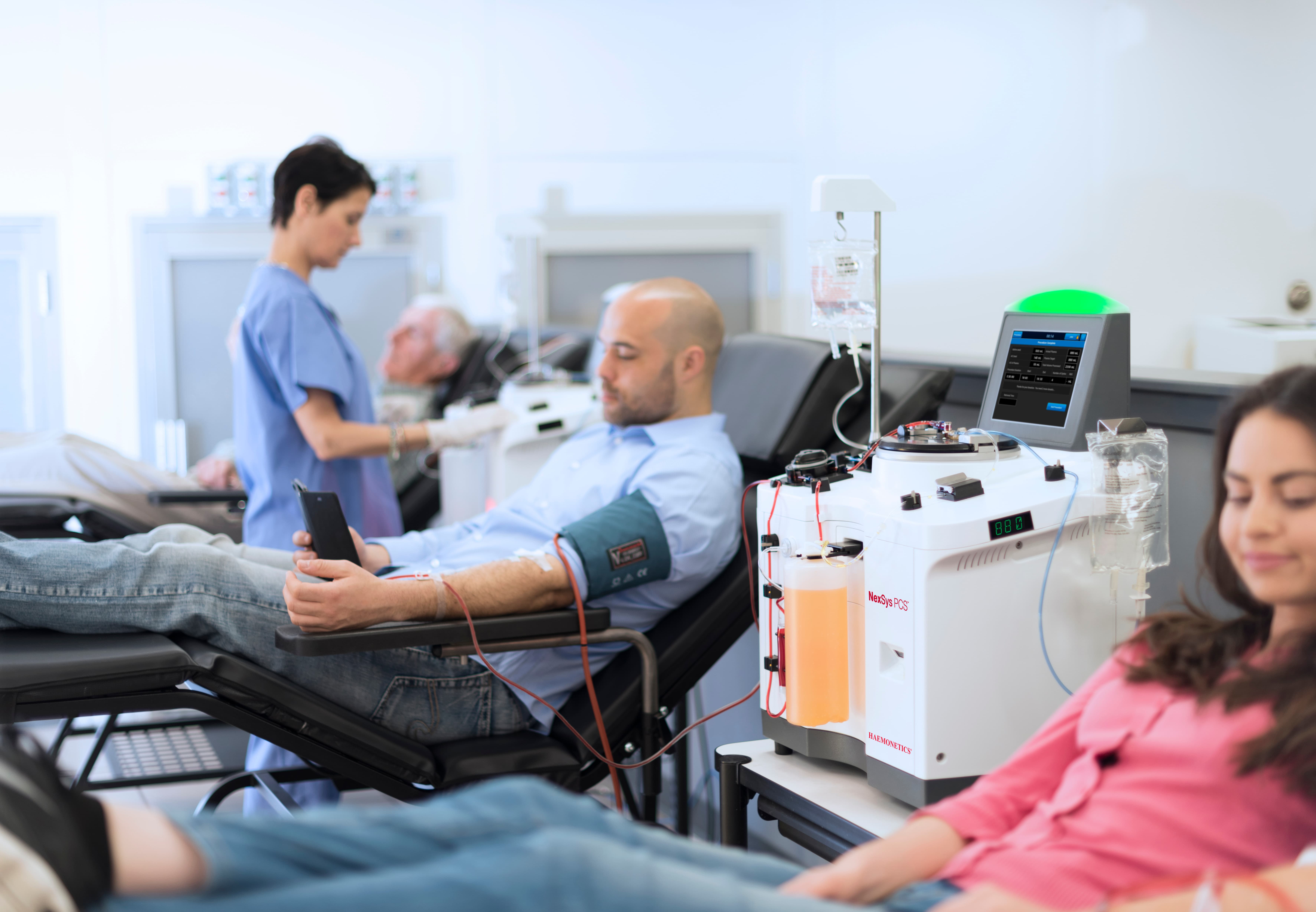
Optimizing Operations for Plasma Centers
We offer innovative technologies that enable higher plasma yield collections, improve productivity and quality in our customers’ centers, and enhance the overall donor experience.
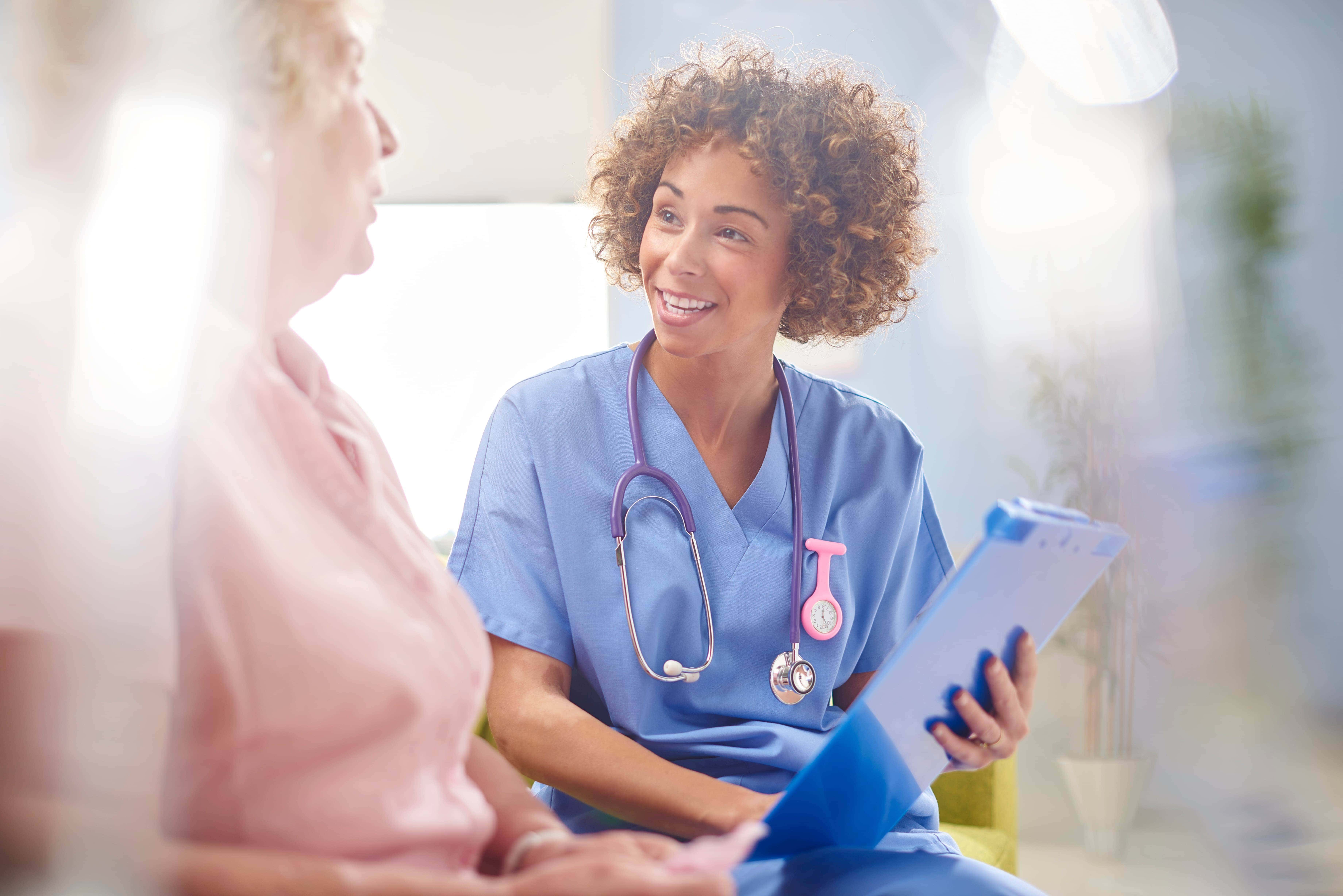

Advancing Patient Care at Hospitals
We provide information and solutions that help enable healthcare professionals to improve patient care and economic outcomes in critical settings.
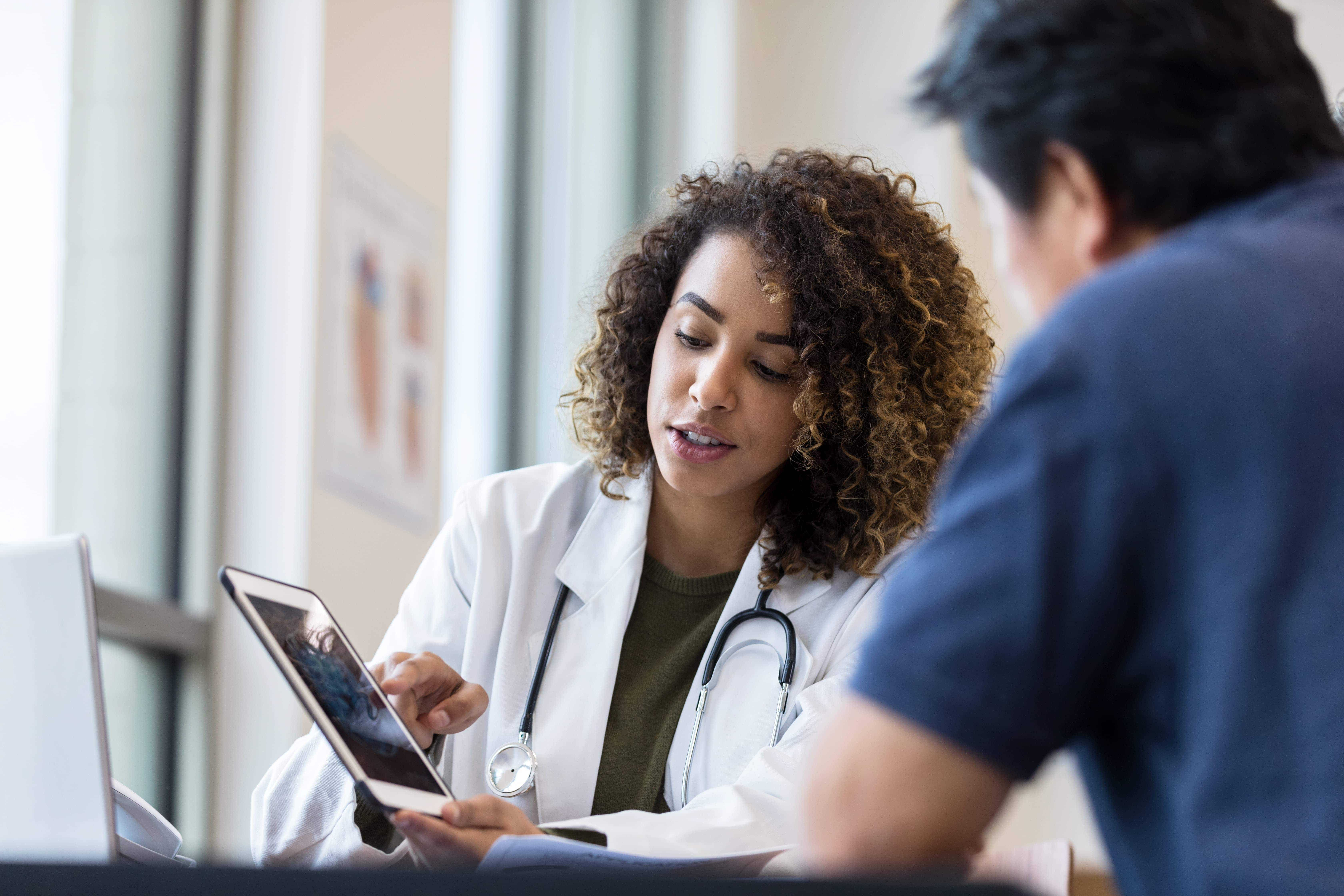

Driving Efficiency for Blood Centers
We advance products and services to help
ensure blood safety, improve operational efficiency and collect the blood components in the greatest demand.

Careers
Join Our Winning Team
At Haemonetics, the work you do matters. Join us in advancing healthcare while you advance your own career and make your ideas, commitment and passion matter every day.

Our Mission
Making Our Work Matter
We develop innovative medical technology products and services that improve the quality, effectiveness and efficiency of care. We are building a collaborative, performance-driven culture that attracts and develops the best talent.

Corporate Responsibility
Guided by Purpose
At Haemonetics, our Purpose inspires the important work we do every day to meaningfully advance patient care and drive greater possibilities in healthcare. How we do this work is equally important. We are guided by our Purpose, and mindful of our shareholders, customers, employees and other key stakeholders whose trust we value. We are committed to being a good corporate citizen and take responsibility to proactively identify and manage the environmental, social and governance risks and opportunities that are relevant to our business and those we serve.
The Latest
View all NewsHaemonetics Sets Date for Publishing Fourth Quarter and Fiscal Year 2024 Results: May 9, 2024
April 10, 2024
Read MoreHaemonetics Receives FDA Clearance for New TEG® 6s Global Hemostasis - HN Cartridge
April 4, 2024
Read MoreHaemonetics Corporation Completes Acquisition of Attune Medical
April 1, 2024
Read MoreHaemonetics Announces Definitive Agreement to Acquire Attune Medical
March 5, 2024
Read More
.jpg?as=0&h=736&hash=E871A5653A3E4857C35BB9BF90F96FB6)